The Boot Process
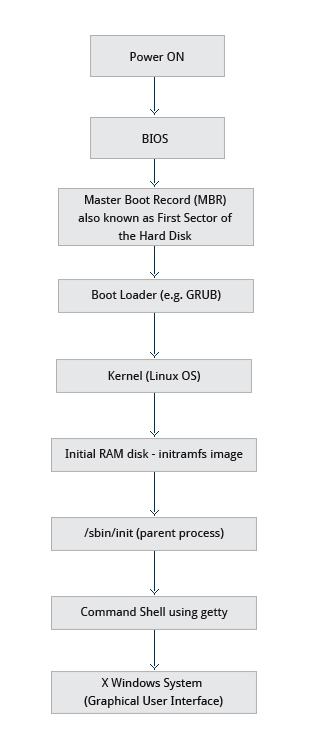
The Linux boot process is the procedure for initializing the system.
from when the computer power is first swithced on until the user interface is fully operational.
having a good understanding of the steps in the boot process may help you with troubleshooting problems, as well as with tailoring the computer’s performance to your needs.
On the other hand, the boot process can be rather technical, and you can start using Linux without knowing all the details.
NOTE: You may want to come back and study this section later, if you want to first get a good feel for how to use a Linux system.
BIOS - The First Step
starting an x86-based Linux system involves a number of stps.
the Basic Input/Output System (BIOS) initializes the hardware, including the screen and keyboard, and tests the main memory.
This process is also called POST (Power On Self Test).
The BIOS software is stored on a ROM chip on the motherboard, After this, the remainder of the boot process is controlled by the operating system (OS).
Master Boot Record (MBR) and Boot Loader
Once the POST is completed -> pass control to boot loader. boot loader is usually stored on one of the hard disks in the system, either in the boot sector (for traditional BIOS/MBR systems). or EFI partition (for more recent (Unified Extensible Firmware interface or EFI/UEFI systems).
boot loader stored in …
- hard disk,
- boot sector,
- EFI partition
thereafter, date,time and the most important peripherals are loaded from CMOS values.
A number of bootloaders exist for Linux;
- GRUB,
- ISOLINUX,
- DAS U-Boot
when booting linux, the bootloader is responsible for loading the kernel image and the initial RAM disk or file system (contains some critical files and device drivers needed to start the system) into memory
Boot Loader in Action
BIOS/MBR system, boot loader resides at the first sector of the hard disk (MBR).
in this stage, boot loader examines partition table and finds the bootable partition
Once it finds bootable partition, it then searches for the second stage boot loader, for example GRUB, and loads it into RAM.
find boot loader from first sector
- examines partition table / find bootable partition
search and loads second stage boot loader (ex. GRUB), and load to RAM
EFI/UEFI system, UEFI firmware reads its Boot Manger data to determine which UEFI application is to be launched and from where (disk, EFI partition)
then launched the UEFI application, for example GRUB, as defined in he boot entry in the firmware’s boot maanger.
this procedure is more complicated, but more versatile than the older MBR methods.
UEFI frimware read boot Manager and find UEFI application
UEFI application launch (ex. GRUB, defined in boot entry in boot manager)
more versatile compaired with MBR
the second stage boot loader resides under /boot. after choosing the OS, the boot loader loads the kernel of the selected operating system into RAM
and passes control to it. Kernels almost always compressed, so its first job is to uncompress it self. after this, check/analyze hardware and initialize drviers.
/boot’s second stage boot loader load kernel and pass control to it.
uncompress / check hardware / and initializes hard drivers.
Initial RAM Disk
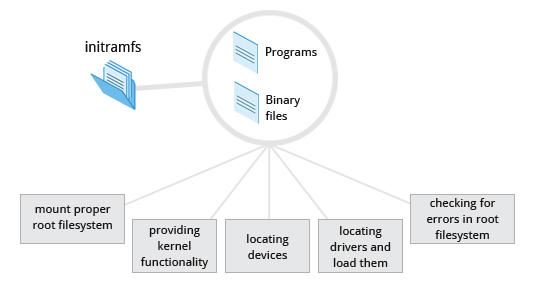
initramfs filesystem image contains programs / and binary files that perform all actions needed to mount the proper root filesystem.
ex.
- providing kernel functionality for the needed filesystem,
- device drivers for mass storage controllers with a facility called
udev(figuraring out which devices are present, locating the device drivers they need to operate propery) - root filesystem has been found, it is checked for errors and mounted.
mount program instructs the operating system that a filesystem is ready for use, and associates it with a perticular point in the overall hierachy of the filesystem (the mount point).
If this is successful,, the initramfs is cleared from RAM and the init program on the root filesystem (/sbin/init) is executed.
init handles the mounting and pivoting over to the final real root filesystem. If special hardware drivers are needed before mass stroage can be accessed, they must be in the initramfs image.
Text-Mode Login
init starts a number of text-mode login prompts. and to eventually get a command shell.
default command shell is bash(the GNU Bourne Again Shell)